A community-based intervention strategy is used where public volunteers are trained and used as research partners. This results in a peer-led follow-up strategy (e.g., through peer reminder calls).
A peer‐led follow‐up strategy may result in a large increase in retention.
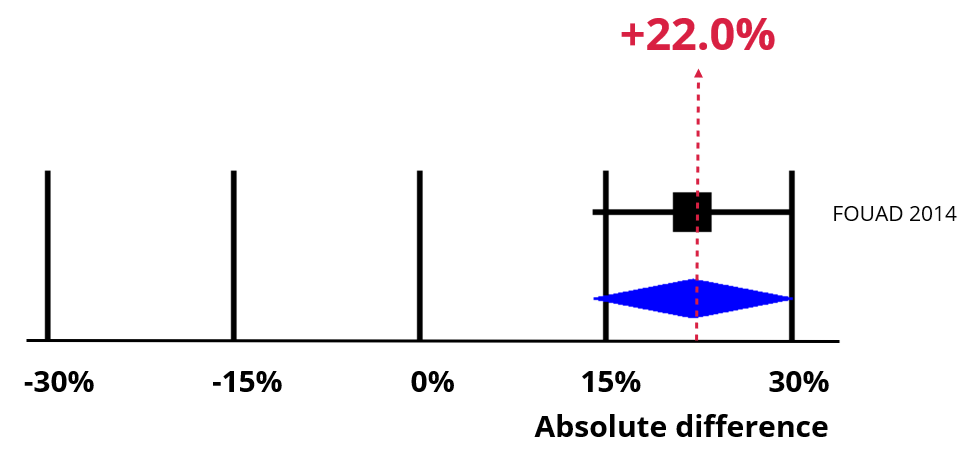
An increase of 22% (95% confidence interval = 14% to 30%).
GRADE Low certainty.
We recommend that trialists consider using a peer-led follow-up strategy.
See Resource bundle below for details on how to implement a peer-led follow-up strategy.
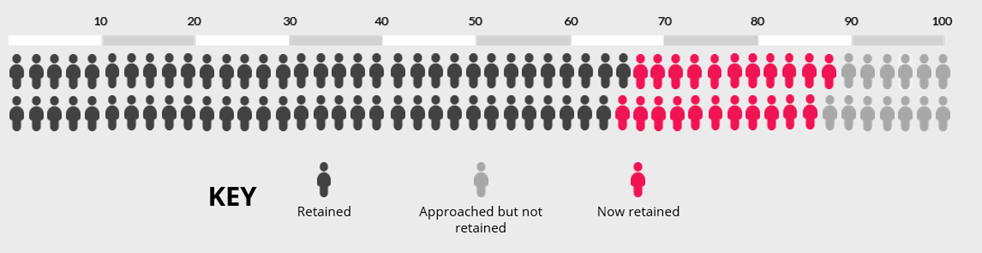
Imagine initial retention is 65% of those approached. You have a trial with 100 participants that needs responses from 80 to meet its statistical power calculations. Retention of 65% means that you will be 15 responses short (see chart below).

Now imagine using a peer-led follow-up strategy. The chart below shows the impact of an absolute increase of 22% (95% CI = 14% to 30%). Retention is now 87%, which means our best estimate is that you would now have enough participants to meet the statistical power calculations.
Trial Forge will make trials more efficient by looking for marginal gains across all trial processes, from research question to implementation into routine care. It will encourage everyone connected with trials to be more sceptical of what we do by asking for the evidence behind all of our trial decisions.